Information leads to transformation.
Isrealmore Ayivor
Diagnostics have come quite a long way in recent years, and the carotid intima-media thickness (CIMT) test is no exception. Nowadays, this noninvasive assessment can give physicians in-depth insights into heart health, accessing information that has traditionally only been available through more invasive means. Moreover, the data gleaned from this test often go overlooked, as the conditions for which CIMT tests aim to identify often present no outward symptoms.
Yet, some patients may wonder if the CIMT test is really necessary. After all, most individuals have never even heard of it, let alone received a referral for one. Is the CIMT test right for you? Discover what it entails and how it could be the very test to unlock life-changing results below.
The CIMT test is often used as a preventive measure to check for serious conditions such as heart disease and stroke. Heart disease often exhibits no symptoms or warning signs, and many people only become aware of their individual risk through biomarkers uncovered by lab work. While in some cases symptoms such as fatigue, irregular heartbeat, and chest pain may be present, in many cases, the first symptom of heart disease is a heart attack. [1]
This is because plaque can slowly and silently build up along the walls of the arteries for many years. While the arteries can become thickened, resulting in what’s known as atherosclerosis, there may be little to no outward sign of a medical issue. Blood pressure changes and elevated C-reactive protein (CRP) levels (identified through blood work) are among the few indicators that might alert physicians to this systemic inflammation.
The CIMT test is used to evaluate the carotid arteries by measuring changes in plaque and the thickness of the vessel walls. Even if no atherosclerosis is present, there could still be changes in artery thickness which can alert doctors to an elevated risk for heart attack or stroke. With this early intervention, medical experts can determine and predict risk for cardiovascular disease or stroke and can subsequently make clinical recommendations to support the best possible patient outcomes.
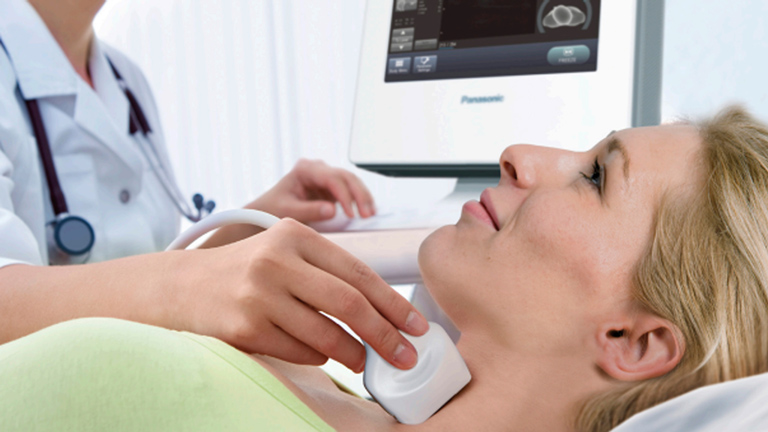
Using ultrasound scanners, sonographers perform CIMT tests, which use sound waves to pinpoint the extent of plaque buildup in the walls of the arteries which supply oxygenated blood to the head. The sound waves are high-frequency and inaudible and are measured by a computer to depict real-time imaging on a monitor.
The carotid intima-media thickness measures two separate layers of the carotid artery: the intima and the media. There are actually two carotid arteries; one on either side of the neck. Because this artery branch supplies blood to the brain, it’s one of the most important systems within the body. Clinically examining these arteries can uncover important evidence of a number of conditions. For instance, inflammation within this artery could suggest an autoimmune condition or previously undetected infection.
An increase in intima-media thickness (IMT) is often the first structural change that can be detected in atherosclerosis. [2] Moreover, the state of the carotid arteries corresponds with the state of the arteries all throughout the body, including those within the heart. Having thicker arteries can increase the risk of developing coronary heart disease, peripheral artery disease, carotid artery disease, and chronic kidney disease. [3]
While aging contributes to thicker carotid intima-media, there are a number of other factors which play a role in the arteries’ thickness:
These can all lead to increased thickness in the carotid intima-media. [4] Although certain behaviors can certainly contribute to increased risk for heart conditions, researchers have determined that CIMT predicts future vascular events independently of conventional risk factors for heart disease or stroke. [5] Thus, while increased IMT may exhibit no outward symptoms at all, it’s among the most powerful predictor of a cardiovascular event — but continues to go overlooked by most practitioners of traditional medicine.
Consider the fact that four times as many fatalities are caused by heart events compared to cancer, and traditional medicine mischaracterized 50% of patients as low-risk who would later experience a heart event [6]. Physicians who employ the CIMT test aim to take a more accurate approach to assess heart attack risk, while also preventing heart events in at-risk populations by offering effective, proactive interventions.
Aside from the fact that research shows the CIMT test to be an effective predictor of future vascular events, there are a number of other advantages of the assessment. [7] For one, CIMT is believed to be valuable for collecting a more refined perspective of an individual’s risk for cardiovascular disease.
For another, the test is non-invasive, requires no blood draws and uses ultrasound waves, which are generally considered safer than many other types of waves. The test itself is fairly quick, and no special preparation is needed on the patient’s part. Likewise, there is no required recovery time, and the test is, therefore, non-disruptive to an individual’s daily lifestyle.
Compare this with other forms of testing used to evaluate heart disease risk. While many of these tests still have their place in certain circumstances, some may present certain challenges. For example, cardiac CT angiograms require the use of contrast dye, to which some individuals have an allergy. Left heart catheterization requires the use of a catheter in the femoral artery in the groin or wrist, which can lead to bleeding or hematoma formation at the site. [8]
Yet, despite the many advantages of CIMT testing, there are some factors to consider before pursuing it. For one, it is only offered in the most modern facilities, as it’s still generally considered cutting-edge technology. Moreover, not all physicians are trained in interpreting the test’s results, which is why it’s critically important to work with a clinical team well-versed in CIMT testing.
The ultrasound exam will be painless and non-invasive, but it’s still a good idea to wear loose-fitting, nonrestrictive clothing so you can stay comfortable during the test. An open-necked shirt is ideal, as the technician will need to access your neck area. There is no other preparation required for the carotid artery test.
The technician will apply a thick gel to the skin, which allows soundwaves to move from the machine into the body with the help of a transducer. As the sound waves bounce off the arteries, echoes are communicated to the transducer. The transducer then creates electronic signals which are processed by the computer. A report will then be generated identifying your unique risk profile.
Results of a CIMT are typically classified into four categories:
Depending on your unique results, your doctor will go over risk factors and generate an individualized treatment plan to help you manage your risk for heart disease or stroke.
Typically, doctors who are familiar with the CIMT will only order the test if a patient is believed to have a moderate risk for heart disease.
Risk factors could include:
Nonetheless, it’s important to bear in mind that patients are often mischaracterized as low-risk. Thus, physicians with a focus on disease prevention are likely to recommend this test as a worthwhile preventive measure for most adults approaching or in their middle ages.
At Cenegenics, our focus is always on helping patients defy their age through practices that help to minimize the risk for serious disease. In particular, heart health is one of our most important priorities, as we know that heart disease is the leading killer in the U.S., and far too many patients go undiagnosed with cardiovascular concerns which could otherwise be addressed proactively. For these reasons, we include the CIMT test in all of our patient evaluations.
Our carotid artery ultrasonography exam is an FDA-approved, non-invasive exam that allows for early detection and proactive strategies to help reduce the risk of catastrophic events. When clinically indicated, our team of expert physicians will empower you to take control of your health with prescriptive lifestyle and diet modifications as needed. In doing so, we give you the tools that will help you cultivate a rich and healthy life well into your retirement as you reclaim your glory days™.
Our world-class physicians create a personalized plan to help you feel 10+ years younger. You’ll be more energetic, lose weight, sleep better, have more libido, and think more clearly. Click below to schedule a free consultation with one of our physicians. It’s quick + easy.
Key Resources
This guide was produced with contributions from the following key resources:
The Cenegenics Education and Research Foundation
The Textbook of Age Management Medicine Volume 1: Mastering Healthy Aging Nutrition, Exercise and Hormone Replacement Therapy
The Cenegenics Education and Research Foundation
The Textbook of Age Management Medicine Volume 2: Mastering Healthy Aging Nutrition, Exercise and Hormone Replacement Therapy
Textbook Authors:
Jeffrey Park Leake, M.D., CPT
Dr. Jeffrey Park Leake is a Partner and Director of Education at Cenegenics Elite Health specializing in age management and wellness. Having trained hundreds of physicians worldwide, Dr. Leake is also the Director of Education for the Clinical Strategies for Healthy Aging course at AMM Educational Foundation.
Todd David Greenberg, M.D., CSCS
Dr. Todd Greenberg is a practicing physician with a broad range of expertise, including wellness, exercise, sports injuries, and MRI of sports injuries. He is a Radiology Clinical Associate Professor at the University of Washington.
Additional Resources
More Than 800,000 Americans Suffer From Heart Disease Every Year. Learn The Symptoms Here:
Recognizing Your Risk Factors of Type 2 Diabetes
More Than 84 Million American’s Are At Risk Of Type 2 Diabetes. See How Cenegenics Can Help
The Link Between Chronic Inflammation & Deadly Diseases
Causes of High Blood Pressure: How to Prevent Hypertension
What is Metabolic Syndrome? Symptoms, Diagnosis & Treatment
References
[1] Mayo Clinic, “Heart Disease.” 22 March 2018. Retrieved from URL: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/heart-disease/symptoms-causes/syc-20353118
[2] Simova, Iana. “Intima-media thickness: Appropriate evaluation and proper measurement, described.” European Society of Cardiology. 05 May 2015. Retrieved from URL: https://www.escardio.org/Journals/E-Journal-of-Cardiology-Practice/Volume-13/Intima-media-thickness-Appropriate-evaluation-and-proper-measurement-described
[3] Rogers, Graham, MD. “What You Should Know About the Carotid Intima-Media Thickness (CIMT) Test.” Healthline. 31 Jan. 2017. Retrieved from URL: https://www.healthline.com/health/heart-disease/cimt-test
[4] Cedars-Sinai. “Carotid Intima-Media Thickness Test (CIMT).” Retrieved from URL: https://www.cedars-sinai.org/programs/heart/clinical/womens-heart/services/cimt-carotid-intima-media-thickness-test.html
[5] Matthias W. Lorenz, et al. “Carotid Intima-Media Thickening Indicates a Higher Vascular Risk Across a Wide Age Range.” Stroke. 8 Dec. 2005.
[6] Vulnerable Plaque to Vulnerable Patient—Part III: Executive Summary of the Screening for Heart Attack Prevention and Education (SHAPE) Task Force Report, The American Journal of Cardiology, 2006.
[7] Matthias W. Lorenz, et al. “Prediction of Clinical Cardiovascular Events With Intima-Media Thickness.” Circulation. 30 Jan. 2007.
[8] Rogers, Graham, MD. See above.
 Contributor: Rudy Inaba Vice President of Health Performance
Contributor: Rudy Inaba Vice President of Health Performance
Rudy Inaba is Cenegenics’ Vice President of Health Performance. He is a recognized fitness and sports nutrition consultant with nearly 15 years of experience in clinical exercise physiology and lifestyle management. After pursuing his Master of Science in Clinical Exercise Physiology at the University of Nevada Las Vegas, Rudy joined Cenegenics where he leads 19 clinical locations nationwide in their advancements in kinesiology, nutritional biochemistry, and their analyses of industry research & market trending.


